Understanding the Connection Between Thyroid Health and Fertility
If you’ve been diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, you are not alone. Approximately 20 million people in the U.S. are affected by thyroid disease, with women being significantly more susceptible than men. According to the American Thyroid Association, one in eight women will develop a thyroid disorder in her lifetime.
Thyroid disease can impact overall health in various ways, including weight fluctuations, hair loss, fatigue, depression, and insomnia. However, it can also have a profound effect on reproductive health. If you’re trying to conceive, understanding your thyroid function is essential, as it may influence your fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
What is the Thyroid Gland?
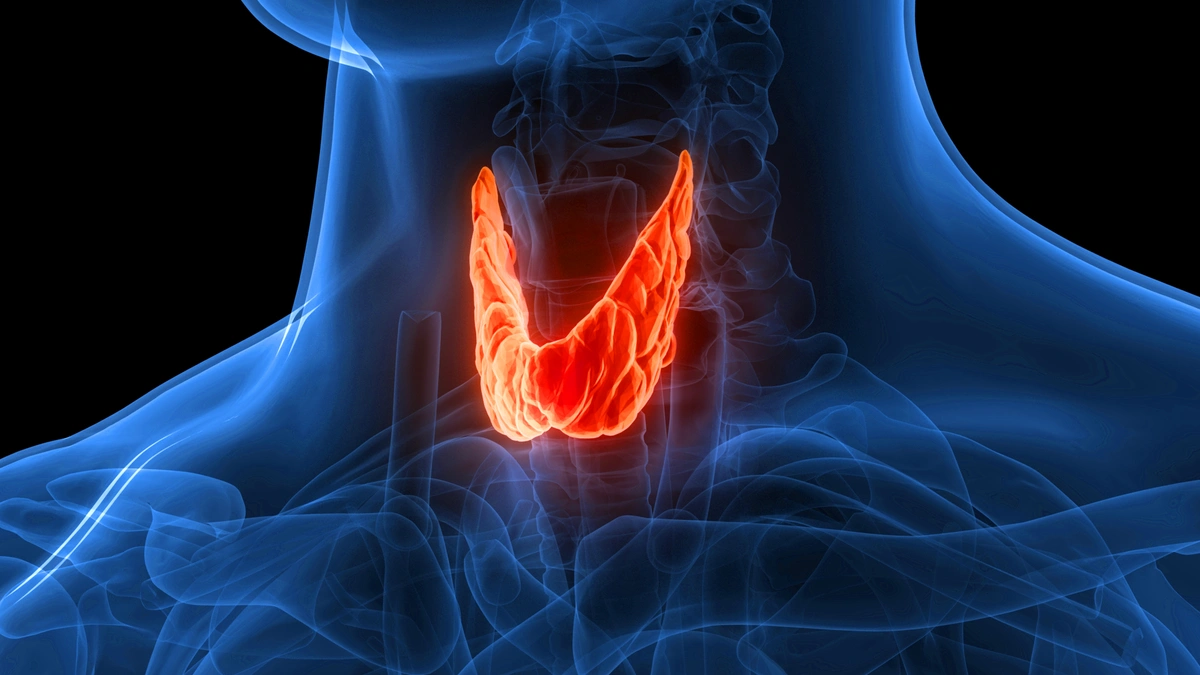
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of your neck, just below the larynx (voice box). As part of the endocrine system, it plays a crucial role in hormone production, helping to regulate metabolism, energy levels, and vital body functions such as breathing, heart rate, and temperature control.
Illustration of the thyroid gland
The thyroid produces two key hormones:
-
Triiodothyronine (T3)
-
Thyroxine (T4)
An imbalance in these hormones—whether too much or too little—can affect the reproductive system, potentially making it harder to conceive.
How Do Thyroid Disorders Affect Fertility?
Thyroid dysfunction generally falls into two categories:
-
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid): Producing too much thyroid hormone.
-
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid): Producing too little thyroid hormone.
Additionally, thyroid nodules or growths may develop. While most nodules are benign, they can sometimes cause swallowing difficulties or contribute to hormonal imbalances.
Hyperthyroidism and Reproductive Health
Excess T3 and T4 in the body can cause symptoms such as:
-
Anxiety and irritability
-
Hand tremors
-
Brittle hair and hair loss
-
Increased appetite with unintended weight loss
-
Sensitivity to heat
-
Rapid heart rate
-
Missed or irregular menstrual cycles
Hyperthyroidism has been linked to fertility challenges. Research has found that women with overactive thyroids can have more trouble conceiving and lower pregnancy chances. Experts recommend that women struggling to conceive or experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss undergo thyroid screening.
Impact on Pregnancy: If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to pregnancy complications such as:
-
High blood pressure during pregnancy
-
Premature birth
-
Low birth weight
-
Increased risk of miscarriage
With proper management, many women with hyperthyroidism can conceive and maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Hypothyroidism and Fertility
When the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, symptoms may include:
-
Depression and difficulty concentrating
-
Dry skin and brittle hair
-
Weight gain
-
Sensitivity to cold
-
Fatigue and sleep disturbances
-
Frequent, heavy menstrual cycles
According to research published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), approximately 2 - 4% of women of reproductive age have hypothyroidism. The condition can disrupt ovulation and menstrual cycles, potentially leading to infertility. It may develop spontaneously, after pregnancy, or following treatment for hyperthyroidism. In some cases, hypothyroidism is congenital.
Impact on Pregnancy: Hypothyroidism increases the risk of:
-
Irregular ovulation or anovulation (lack of ovulation)
-
Increased miscarriage risk
-
Developmental issues in the baby
With proper treatment, hormone levels can be stabilized, improving fertility outcomes and pregnancy health.
Thyroid Disease and Male Infertility
Though commonly associated with women, thyroid disorders can also affect male fertility. An underactive thyroid in men may contribute to:
-
Low sperm count and poor semen quality
-
Reduced testicular function
-
Erectile dysfunction
-
Decreased libido
Studies show that restoring normal thyroid hormone levels can improve sperm health and reproductive function over time.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect thyroid dysfunction, consult with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. Diagnosis typically involves:
-
Blood tests to measure T3, T4, and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) levels
-
Ultrasound imaging for thyroid nodules (if necessary)
-
Additional autoimmune testing for conditions like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease
Treatment Options:
-
Hyperthyroidism: Medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery (in severe cases)
-
Hypothyroidism: Daily thyroid hormone replacement therapy
For those undergoing fertility treatments, thyroid health plays a critical role in success rates. Optimizing thyroid function may increase your chances of conception and reduce miscarriage risk.
When to Seek Help from a Fertility Specialist
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, you should consult a fertility specialist in the following situations:
-
You are under 35 and have been trying to conceive for 12 months without success.
-
You are over 35 and have been trying for six months without success.
-
You have experienced two or more miscarriages.
Addressing thyroid health early can improve fertility outcomes and support a healthy pregnancy journey. Patients should be sure to inform their fertility provider about any thyroid issues, as proper management can enhance their chances of conception and reduce potential pregnancy complications.
Final Thoughts
Thyroid health is a key factor in reproductive wellness. If you’re struggling with infertility, consider having your thyroid function evaluated as part of your fertility assessment. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many individuals with thyroid disorders go on to achieve successful pregnancies and healthy births.
If you have concerns about your fertility or thyroid health, reach out to one of our specialists to discuss the next steps toward growing your family.